This entry shows usefule kubectl commands that I find very useful and use almost every day when working with in the kubernete environment.
Pre Text
What is Kubernetes
Kubernetes, often called k8s, is an open-source platform to automate cicd or containerized applications. It was originally developed by Google.
Key Features and Components
- Containers and Pods
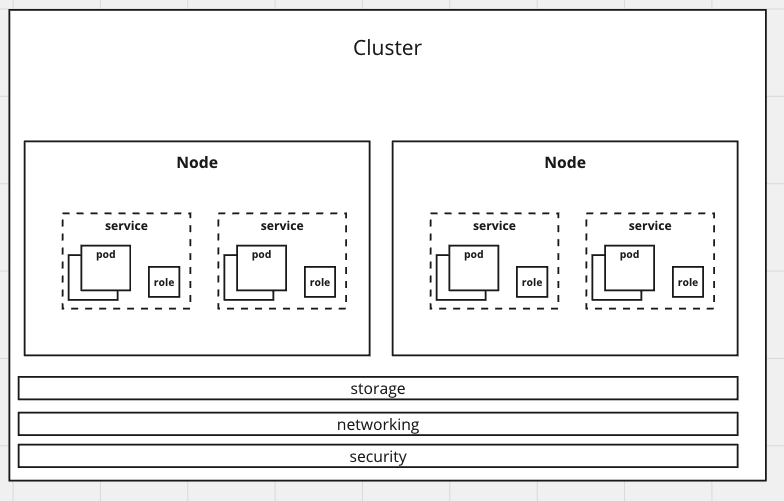
- Cluster Architecture
- Master Components
- Node Components
- Networking
- Storage
- Self-healing
- Scalability and Load Balancing
- Automation
What is Docker
In this article, I will list helpful commands for a developer who works with k8s environment from your local dev machine.
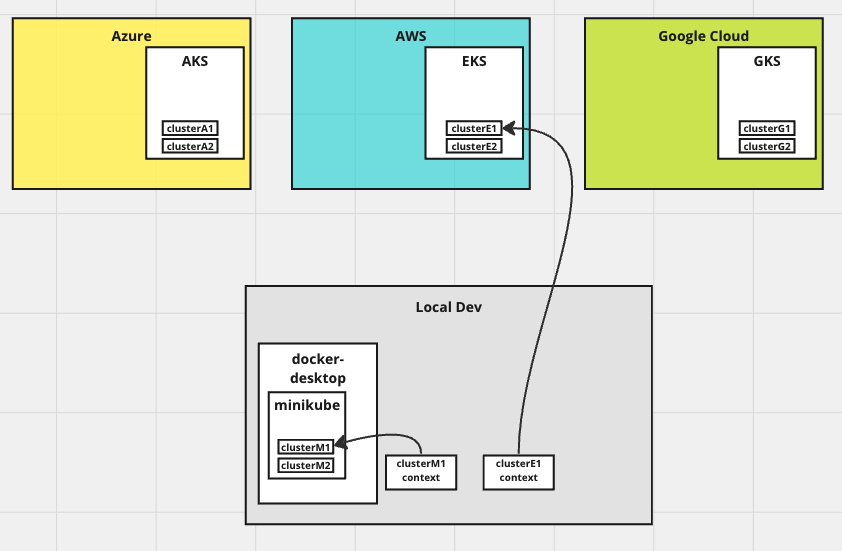
Get Contexts
Get all available contexts
kubectl config get-contextsSee current context
kubectl config current-contextSet current context
kubectl config use-context <context-name>Cluster
To get cluster-info
kubectl cluster-infoTo display resource usage
kubectl top
kubectl top podsGeneral Resources
List resources:
kubectl getDescribe a resource
kubectl describeDescribe the nodes
kubectl describe nodesServices
List services for all namespaces
kubectl get services --all-namespaces
or
kubectl get svc --all-namespacesTo get services for just a namespace
kubectl get services -n <namespace>Pods
Get current pods (in the current context)
kubectl get podsDescribe a specific pod
kubectl describe pod <pod-name>Execute a Command inside a container
kubectl exec -it my-pod -- /bin/bash
root@my-pod:/# ls
bin dev home root var etc
root@my-pod:/# exit
Get logs of a pod
kubectl logs my-pod -c my-containerPort Forward
This example show forwarding local port 5000 to the pod’s port 6000
kubectl port-forward my-pod 5000:6000
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:5000 -> 6000
Forwarding from [::1]:5000 -> 6000