In this article, I documented my steps to set up RayService on my ubunto laptop and I hope it will be useful for someone. This article goes through
- setting up a cluster,
- installing kubeRay operator,
- installing KubeService,
- sending requests to KubeService.
If you have not set up your kubernetes environment, checkout Use Kind and K9s to Learn Kubernetes Locally (on Ubuntu)
Environment
Before Setup
The steps in this entry has been veriried on my MSI Raider Ge68 HX 13V laptop,
On a linux machine, to check the hardware devices (including gpu), do
lspci -v
lspci -v | grep nvidiaTerminology
Ray:
Ray is an open-source unified framework for scaling AI and Python applications like machine learning.
Ray Cluster:
A Ray cluster is a set of worker nodes connected to a common Ray head node. Ray clusters can be fixed-size, or they may autoscale up and down according to the resources requested by applications running on the cluster.
Ray Service:
A RayService manages these components:
- RayCluster: Manages resources in a Kubernetes cluster.
- Ray Serve Applications: Manages users’ applications.
Tools
- kubectl, kind, k9s (see the “Use kind and k9s…” doc shown above)
- helm
- jq
To install helm
Assume you have brew install on Linux (if not, see Use Kind and K9s to Learn Kubernetes Locally (on Ubuntu)
brew install helm
brew install jqInstall Ray
For machine learning application
pip install -U "ray[data,train,tune,serve]"For general Python application
pip install -U "ray[default]"To confirm that ray is set up
ray --versionStart ray cluster locally by starting a head node
ray start --headThen you can follow the output instruction, and hit localhost:8265 to view the dashboard
You can also send command to the head node like this
Set up RayService in a Kubernetes Cluster
Step 1: Create a cluster (using kind)
kind create cluster --image=kindest/node:v1.23.0Create KubeRay Operator
Step 2: Create KubeRay Operator
helm repo add kuberay https://ray-project.github.io/kuberay-helm/
helm repo update
# Install both CRDs and KubeRay operator v1.0.0.
helm install kuberay-operator kuberay/kuberay-operator --version 1.0.0
# Confirm that the operator is running in the namespace `default`.
kubectl get podsStep 3: Install RayService
# Step 3.1: Download `ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml`
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ray-project/kuberay/v1.0.0/ray-operator/config/samples/ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
# Step 3.2: Create a RayService
kubectl apply -f ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yamlStep 4: Verify Kubernetes Cluster Status
# Step 4.1: List all RayService custom resources in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get rayservice
# Step 4.2: List all RayCluster custom resources in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get raycluster
# Step 4.3: List all Ray Pods in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get pods -l=ray.io/is-ray-node=yesWait for the service to come up (around 5 minutes on my laptop). Once all is ready, you should see three namespace shown similar to the example output shown below. There will be a rayservice-sample-head-svc namespace, and rayservice-sample-serve-svc namespace. You raycluster-xxxx-head-svc will have different xxxx than what’s shown below.
# Step 4.4: List services in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get services
# NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP
# ...
# rayservice-sample-head-svc ClusterIP 10.96.34.90
# rayservice-sample-raycluster-6mj28-head-svc ClusterIP 10.96.171.184
# rayservice-sample-serve-svc ClusterIP 10.96.161.84 You can use this helper script until these three components are up:
while true; do
kubectl get services
sleep 5
doneStep 5: Verify the status of the Serve Applications
kubectl port-forward svc/rayservice-sample-head-svc --address 0.0.0.0 8265:8265You should be able to visit the ray dashboard and see the fruit service is now deployed
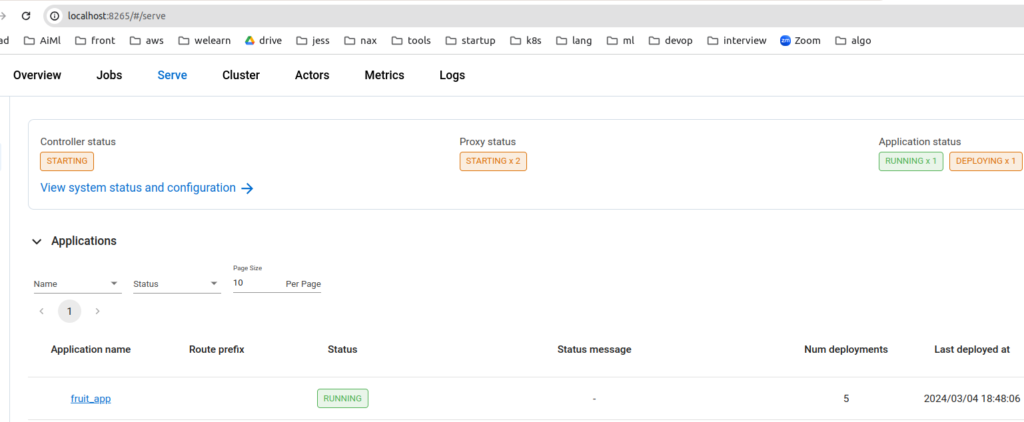
Send Request to Ray Service
Step 6: Send request
# Step 6.1: Run a curl Pod.
# If you already have a curl Pod, you can use `kubectl exec -it <curl-pod> -- sh` to access the Pod.
kubectl run curl --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -i --tty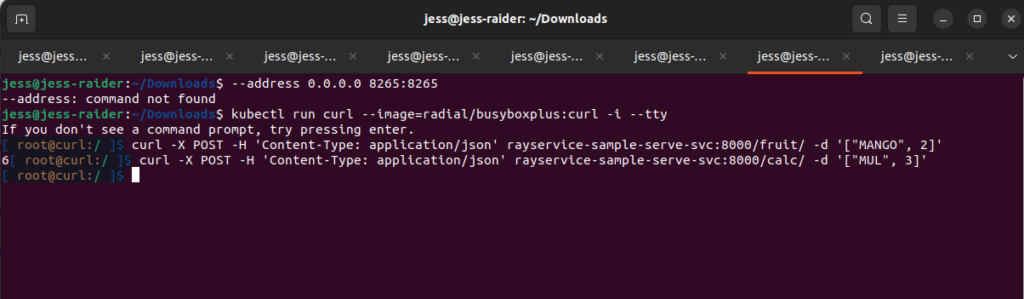
Then at the terminal run
# Step 6.2: Send a request to the fruit stand app.
[ root@curl:/ ] curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' rayservice-sample-serve-svc:8000/fruit/ -d '["MANGO", 2]'
# [Expected output]: 6
# Step 6.3: Send a request to the calculator app.
[ root@curl:/ ] curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' rayservice-sample-serve-svc:8000/calc/ -d '["MUL", 3]'
# [Expected output]: "15 pizzas please!"References
https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/cluster/kubernetes/getting-started.html